Motherboard Components: What Features do all Motherboards share in 2024?
Motherboard Components
Introduction: So what do all those motherboard components do?
I started out on the world of personal computing back in 1982 when I got my first IBM monstrosity. I was always curious as to what all those motherboard components did? This curiosity spurred me on to have a very lucrative IT career working for some of the largest companies in the world.
So what’s changed in the makeup of a motherboard? Well, nothing really, everything got smaller and faster but the basic components that make up a motherboard mostly stayed the same.
So what motherboard components make up the latest boards of today?
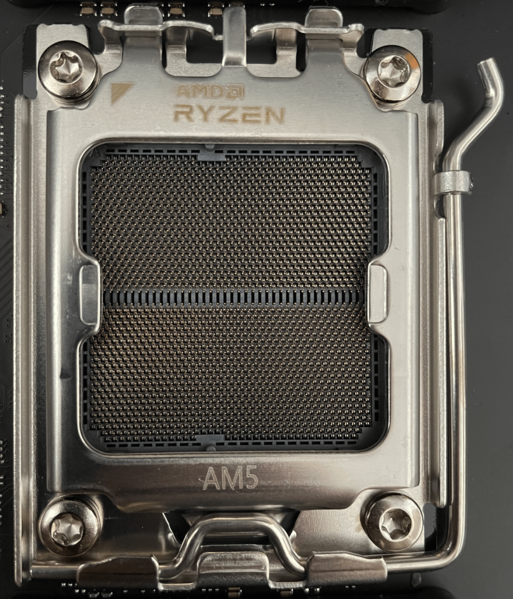
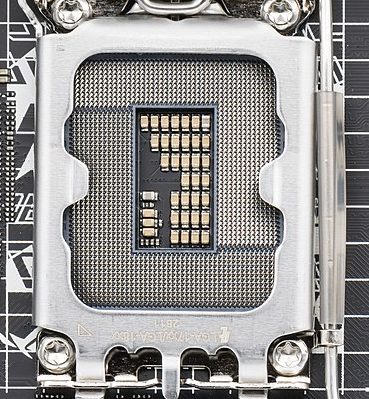
CPU Socket
This is the slot on the motherboard where the central processing unit (CPU) is physically installed. The socket type determines which CPUs are compatible with the motherboard.
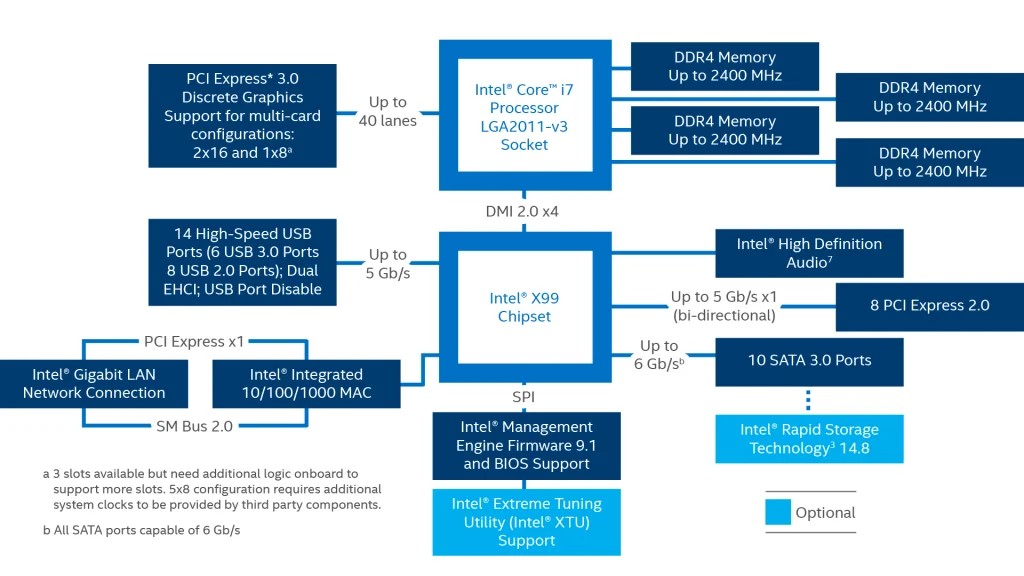
Chipset
The chipset is a group of integrated circuits that manages the communication between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other peripherals. It acts as a bridge between these components, ensuring they all work together seamlessly.
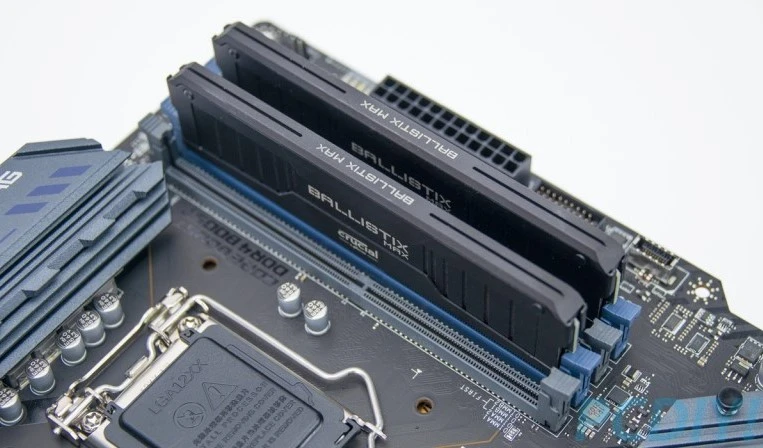
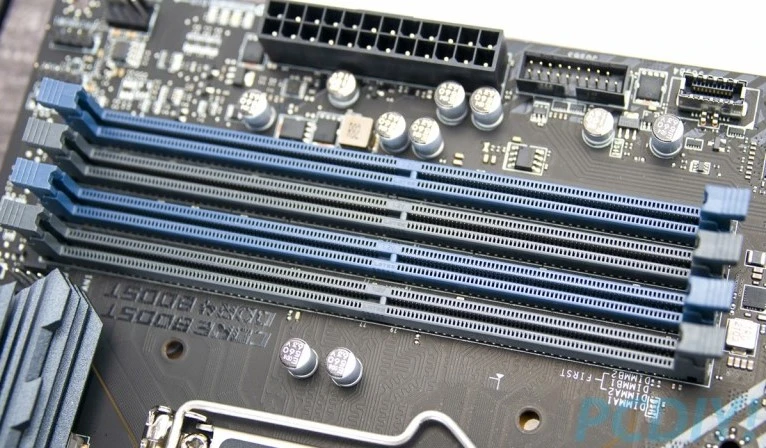
Memory Slots
These slots are where the random access memory (RAM) modules are inserted. RAM provides temporary storage for data that the CPU is actively using. The number of memory slots and the type of RAM supported will vary depending on the motherboard.
Expansion Slots
These slots allow you to add additional hardware components to your computer, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. The most common type of expansion slot is PCI Express (PCIe), which provides high-speed bandwidth for modern peripherals.
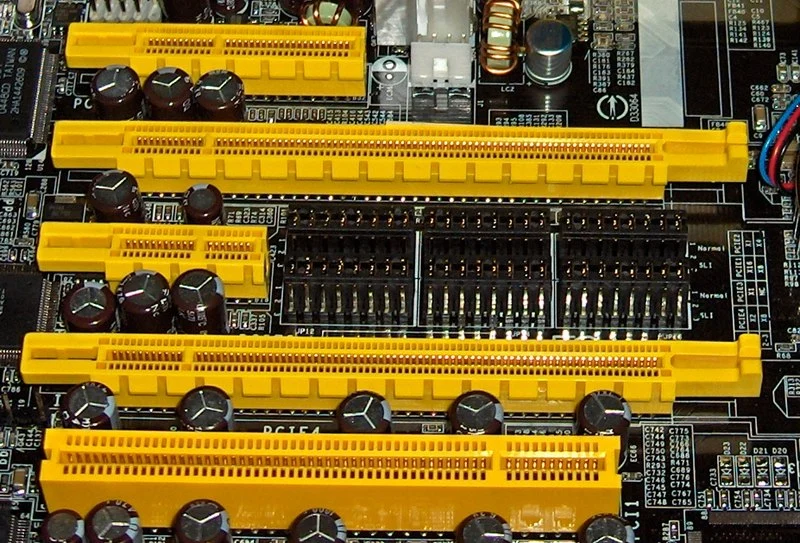
Bus
A bus is a communication pathway that allows data to be transferred between different components on the motherboard. There are several different types of buses used on motherboards, such as the front-side bus (FSB) and the memory bus.
Power Connectors
The motherboard requires power from the power supply unit (PSU) in order to function. There are two main power connectors: the 24-pin ATX connector and the 4/8-pin EPS connector. The 24-pin ATX connector supplies power to the motherboard itself, while the 4/8-pin EPS connector supplies additional power to the CPU.

Input/Output (I/O) Ports
These ports are located on the back panel of the motherboard and provide a way to connect external devices to your computer, such as monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and USB devices.
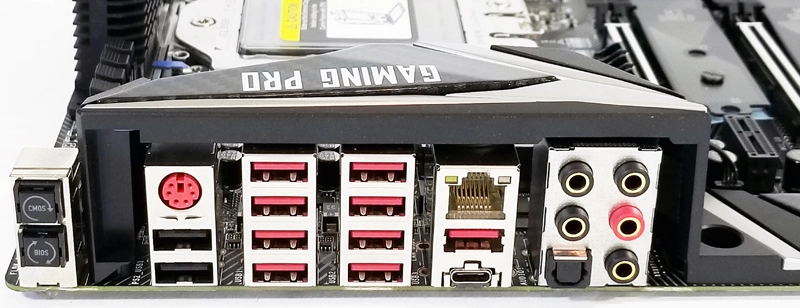
These are just some of the most common technologies that all motherboards share. The specific features and capabilities of a motherboard will vary depending on its design, target market, and price point. I will go into more detail in other documents on this website and link them here.